Wiki test: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
<!-- Center Banner --> | |||
<div style="display: flex; justify-content: space-between; margin-bottom: 10px;"> | <div style="display: flex; justify-content: space-between; margin-bottom: 10px;"> | ||
<div style="width: 95%; padding-right: 20px;"> | <div style="width: 95%; padding-right: 20px;"> | ||
| Line 14: | Line 15: | ||
<!-- Left Column --> | <!-- Left Column --> | ||
<div style="width: 50%; padding-right: 10px;"> | <div style="width: 50%; padding-right: 10px;"> | ||
<div class="MainPageBG" style="border: 1px solid #d7d7d7; padding: 10px; background-color: #f9f9f9;"> | <div class="MainPageBG" style="border: 1px solid #d7d7d7; padding: 10px; background-color: #f9f9f9;"> | ||
<h2>UW Climate Risk Lab</h2 | <h2 style="font-family: 'Helvetica', Arial, sans-serif; | ||
font-weight: bold; font-size: 21px">UW Climate Risk Lab</h2> | |||
<p>The UW Climate Risk Lab (CRL) is a multidisciplinary research and innovation center based at the [https://foster.uw.edu/ University of Washington Foster School of Business] in the Department of Finance & Business Economics | <p>The UW Climate Risk Lab (CRL) is a multidisciplinary research and innovation center based at the [https://foster.uw.edu/ University of Washington Foster School of Business] in the Department of Finance & Business Economics. <p> | ||
<p>The CRL brings together academics and professionals in climate finance, risk management, business | |||
<p>The CRL brings together academics and professionals in climate finance, risk management, business | |||
analytics, data engineering, computer science, atmospheric sciences, supply chains management, | analytics, data engineering, computer science, atmospheric sciences, supply chains management, | ||
information systems and AI | information systems and AI. </p> | ||
<div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" data-expandtext="Read more" data-collapsetext="Read less"> | |||
<h3>History</h3> | |||
<p>The CRL originated in 2022 with a grant from the Office of UW President</p> | |||
</div> | |||
: | <div style="clear: both;"></div> | ||
</div> <!-- close minipage of left column --> | |||
<div class="MainPageBG" style="border: 1px solid #d7d7d7; padding: 10px; background-color: #f9f9f9;"> | <div class="MainPageBG" style="border: 1px solid #d7d7d7; padding: 10px; background-color: #f9f9f9;"> | ||
<h2>License Information</h2> | <h2 style="font-family: 'Helvetica', Arial, sans-serif; | ||
<p> | font-weight: bold; font-size: 21px">License Information</h2> | ||
This website’s content is licensed under a [https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License].</p> | <p>This website’s content is licensed under a [https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/Creative Commons | ||
Attribution 4.0 International License].</p> | |||
'''You are free to: ''' | '''You are free to: ''' | ||
| Line 62: | Line 45: | ||
* Adapt — remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially. | * Adapt — remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially. | ||
:The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms. | |||
<div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" data-expandtext="Read more" data-collapsetext="Read less"> | |||
'''Under the following terms:''' | '''Under the following terms:''' | ||
| Line 69: | Line 54: | ||
* No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits. | * No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits. | ||
'''Notices:''' | |||
* You do not have to comply with the license for elements of the material in the public domain or where your use is permitted by an applicable exception or limitation. | |||
* No warranties are given. The license may not give you all of the permissions necessary for your intended use. For example, other rights such as publicity, privacy, or moral rights may limit how you use the material. | |||
Read the full license [https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ here]. | Read the full license [https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ here]. | ||
</div> | |||
<div style="clear: both;"></div> | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 78: | Line 69: | ||
<!-- Did you know Section --> | <!-- Did you know Section --> | ||
<div class="MainPageBG" style="border: 1px solid #d7d7d7; padding: 10px; background-color: #f9f9f9;"> | <div class="MainPageBG" style="border: 1px solid #d7d7d7; padding: 10px; background-color: #f9f9f9;"> | ||
= | <h2 style="font-family: 'Helvetica', Arial, sans-serif; | ||
font-weight: bold; font-size: 21px">Climate-related Financial Risk | |||
=== What is climate risk? === | === What is climate risk? === | ||
Climate risk is the potential for negative consequences for human or ecological systems from the [[wikipedia:Impacts_of_Climate_Change|impacts of climate change]]. <ref>IPCC, 2022: Annex II: Glossary [Möller, V., R. van Diemen, J.B.R. Matthews, C. Méndez, S. Semenov, J.S. Fuglestvedt, A. Reisinger (eds.)]. In: Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [H.-O.Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke, V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA, pp. 2897–2930, doi:10.1017/9781009325844.029.</ref> It refers to risk assessments based on formal analysis of the consequences, likelihoods and responses to these impacts and how societal constraints shape [[wikipedia:Climate_change_adaptation|adaptation]] options. <ref>Adger WN, Brown I, Surminski S (June 2018). "Advances in risk assessment for climate change adaptation policy". Philosophical Transactions. Series A, Mathematical, Physical, and Engineering Sciences. 376 (2121): 20180106. Bibcode:2018RSPTA.37680106A. doi:10.1098/rsta.2018.0106. PMC 5938640. PMID 29712800.</ref> <ref>Eckstein D, Hutfils M, Winges M (December 2018). Global Climate Risk Index 2019; Who Suffers Most From Extreme Weather Events? Weather-related Loss Events in 2017 and 1998 to 2017 (PDF) (14th ed.). Bonn: Germanwatch e.V. p. 35. ISBN 978-3-943704-70-9. Retrieved 7 December 2019.</ref> The science also recognizes different values and preferences around risk, and the importance of risk perception. <ref>Ara Begum, R., R. Lempert, E. Ali, T.A. Benjaminsen, T. Bernauer, W. Cramer, X. Cui, K. Mach, G. Nagy, N.C. Stenseth, R. Sukumar, and P. Wester, 2022: Chapter 1: Point of Departure and Key Concepts. In: Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [H.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke, V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA, pp. 121–196, doi:10.1017/9781009325844.003.</ref> | Climate risk is the potential for negative consequences for human or ecological systems from the [[wikipedia:Impacts_of_Climate_Change|impacts of climate change]]. <ref>IPCC, 2022: Annex II: Glossary [Möller, V., R. van Diemen, J.B.R. Matthews, C. Méndez, S. Semenov, J.S. Fuglestvedt, A. Reisinger (eds.)]. In: Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [H.-O.Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke, V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA, pp. 2897–2930, doi:10.1017/9781009325844.029.</ref> It refers to risk assessments based on formal analysis of the consequences, likelihoods and responses to these impacts and how societal constraints shape [[wikipedia:Climate_change_adaptation|adaptation]] options. <ref>Adger WN, Brown I, Surminski S (June 2018). "Advances in risk assessment for climate change adaptation policy". Philosophical Transactions. Series A, Mathematical, Physical, and Engineering Sciences. 376 (2121): 20180106. Bibcode:2018RSPTA.37680106A. doi:10.1098/rsta.2018.0106. PMC 5938640. PMID 29712800.</ref> <ref>Eckstein D, Hutfils M, Winges M (December 2018). Global Climate Risk Index 2019; Who Suffers Most From Extreme Weather Events? Weather-related Loss Events in 2017 and 1998 to 2017 (PDF) (14th ed.). Bonn: Germanwatch e.V. p. 35. ISBN 978-3-943704-70-9. Retrieved 7 December 2019.</ref> The science also recognizes different values and preferences around risk, and the importance of risk perception. <ref>Ara Begum, R., R. Lempert, E. Ali, T.A. Benjaminsen, T. Bernauer, W. Cramer, X. Cui, K. Mach, G. Nagy, N.C. Stenseth, R. Sukumar, and P. Wester, 2022: Chapter 1: Point of Departure and Key Concepts. In: Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [H.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke, V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA, pp. 121–196, doi:10.1017/9781009325844.003.</ref> | ||
<div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" data-expandtext="Read more" data-collapsetext="Read less"> | |||
Common approaches to [[wikipedia:Risk_assessment|risk assessment]] and [[wikipedia:Risk_management|risk management]] strategies based on [[wikipedia:Natural_Hazards|natural hazards]] have been applied to climate change impacts although there are distinct differences. Based on a [[wikipedia:Climate_system|climate system]] that is no longer staying within a stationary range of extremes, <ref>IPCC (2018). Global Warming of 1.5°C. An IPCC Special Report. Summary for Policymakers (PDF). Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. p. 5.</ref> climate change impacts are anticipated to increase for the coming decades. Ongoing changes in the climate system complicate assessing risks. Applying current knowledge to understand climate risk is further complicated due to substantial differences in regional climate projections. There is also an expanding number of climate model results, and the need to select a useful set of future [[wikipedia:Climate_change_scenario|climate change scenarios]] in the assessments.<ref>Whetton P, Hennessy K, Clarke J, McInnes K, Kent D (2012-12-01). "Use of Representative Climate Futures in impact and adaptation assessment". Climatic Change. 115 (3): 433–442. Bibcode:2012ClCh..115..433W. doi:10.1007/s10584-012-0471-z. S2CID 153833090</ref> | |||
Common approaches to [[wikipedia:Risk_assessment|risk assessment]] and [[wikipedia:Risk_management|risk management]] strategies based on [[wikipedia:Natural_Hazards|natural hazards]] have been applied to climate change impacts although there are distinct differences. Based on a [[wikipedia:Climate_system|climate system]] that is no longer staying within a stationary range of extremes, <ref>IPCC (2018). Global Warming of 1.5°C. An IPCC Special Report. Summary for Policymakers (PDF). Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. p. 5.</ref> climate change impacts are anticipated to increase for the coming decades. Ongoing changes in the climate system complicate assessing risks. Applying current knowledge to understand climate risk is further complicated due to substantial differences in regional climate projections. There is also an expanding number of climate model results, and the need to select a useful set of future [[wikipedia:Climate_change_scenario|climate change scenarios]] in the assessments.<ref>Whetton P, Hennessy K, Clarke J, McInnes K, Kent D (2012-12-01). "Use of Representative Climate Futures in impact and adaptation assessment". Climatic Change. 115 (3): 433–442. Bibcode:2012ClCh..115..433W. doi:10.1007/s10584-012-0471-z. S2CID 153833090</ref> | |||
The [[wikipedia:Intergovernmental_Panel_on_Climate_Change|Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change]] (IPCC) assessment framework is based on the understanding that climate risk emerges from the interaction of three risk factors: [[wikipedia:Hazard|hazards]], [[wikipedia:Climate_change_vulnerability|vulnerability]] and exposure. The IPCC summarizes published research on climate risk evaluations. <ref>About — IPCC". Retrieved 2023-11-16.</ref> International and research communities have been working on various approaches to [[wikipedia:Climate_risk_management|climate risk management]] including [[wikipedia:Climate_risk_insurance|climate risk insurance]]. | The [[wikipedia:Intergovernmental_Panel_on_Climate_Change|Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change]] (IPCC) assessment framework is based on the understanding that climate risk emerges from the interaction of three risk factors: [[wikipedia:Hazard|hazards]], [[wikipedia:Climate_change_vulnerability|vulnerability]] and exposure. The IPCC summarizes published research on climate risk evaluations. <ref>About — IPCC". Retrieved 2023-11-16.</ref> International and research communities have been working on various approaches to [[wikipedia:Climate_risk_management|climate risk management]] including [[wikipedia:Climate_risk_insurance|climate risk insurance]]. | ||
| Line 102: | Line 92: | ||
''Source: [https://assets.bbhub.io/company/sites/60/2021/10/FINAL-2017-TCFD-Report.pdf Recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures]'' | ''Source: [https://assets.bbhub.io/company/sites/60/2021/10/FINAL-2017-TCFD-Report.pdf Recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures]'' | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class=" | |||
<div style="clear: both;"></div> | |||
</div> | |||
<div class="MainPageBG" style="border: 1px solid #d7d7d7; padding: 10px; background-color: #f9f9f9;"> | |||
<h2 style="font-family: 'Helvetica', Arial, sans-serif; | |||
font-weight: bold; font-size: 21px">Data</h2> | |||
</div> | |||
</div> | |||
</div> | |||
<!-- Place the references tag outside of the div --> | |||
<div style="clear: both; width: 100%;"> | |||
<div style="display: flex; justify-content: space-between; margin-bottom: 10px;"> | |||
<div style="width: 95%; padding-right: 20px;"> | |||
== References == | |||
<references /> | |||
</div> | |||
</div> | |||
</div> | |||
Latest revision as of 18:21, 16 September 2024
Welcome to UW Climate Risk Lab Wiki,
the place for best climate risk data, analysis, and tools available for all.
UW Climate Risk Lab
The UW Climate Risk Lab (CRL) is a multidisciplinary research and innovation center based at the University of Washington Foster School of Business in the Department of Finance & Business Economics.
The CRL brings together academics and professionals in climate finance, risk management, business analytics, data engineering, computer science, atmospheric sciences, supply chains management, information systems and AI.
History
The CRL originated in 2022 with a grant from the Office of UW President
License Information
This website’s content is licensed under a [https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License].
You are free to:
- Share — copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format for any purpose, even commercially.
- Adapt — remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
- The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms.
Under the following terms:
- Attribution — You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.
Notices:
- You do not have to comply with the license for elements of the material in the public domain or where your use is permitted by an applicable exception or limitation.
- No warranties are given. The license may not give you all of the permissions necessary for your intended use. For example, other rights such as publicity, privacy, or moral rights may limit how you use the material.
Read the full license here.
What is climate risk?
Climate risk is the potential for negative consequences for human or ecological systems from the impacts of climate change. [1] It refers to risk assessments based on formal analysis of the consequences, likelihoods and responses to these impacts and how societal constraints shape adaptation options. [2] [3] The science also recognizes different values and preferences around risk, and the importance of risk perception. [4]
Common approaches to risk assessment and risk management strategies based on natural hazards have been applied to climate change impacts although there are distinct differences. Based on a climate system that is no longer staying within a stationary range of extremes, [5] climate change impacts are anticipated to increase for the coming decades. Ongoing changes in the climate system complicate assessing risks. Applying current knowledge to understand climate risk is further complicated due to substantial differences in regional climate projections. There is also an expanding number of climate model results, and the need to select a useful set of future climate change scenarios in the assessments.[6]
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) assessment framework is based on the understanding that climate risk emerges from the interaction of three risk factors: hazards, vulnerability and exposure. The IPCC summarizes published research on climate risk evaluations. [7] International and research communities have been working on various approaches to climate risk management including climate risk insurance.
Climate change is a medium- to long-term trend that is expected to have significant financial impacts on companies in affected industries, including on their credit profiles and/or share prices. However, this knowledge is not particularly helpful for lenders, investors, or regulators unless these climate-related financial risks can be further defined in terms of their scope and, more importantly, their timing and likelihood. It is necessary to identify climate risks to industries before they cause reductions in asset utilization or valuation, reduced income and margins, or other financial impacts—changes that translate into credit risk and influence lenders’ decisions about financial profiles. [8]
There are two categories of climate-related financial risk, according to the Taskforce on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD): [9]
- Transition Risks: Risks related to the transition to a lower-carbon economy. (Read more ...)
- Physical Risks: Risks related to the physical impacts of climate change. (Read more ...)
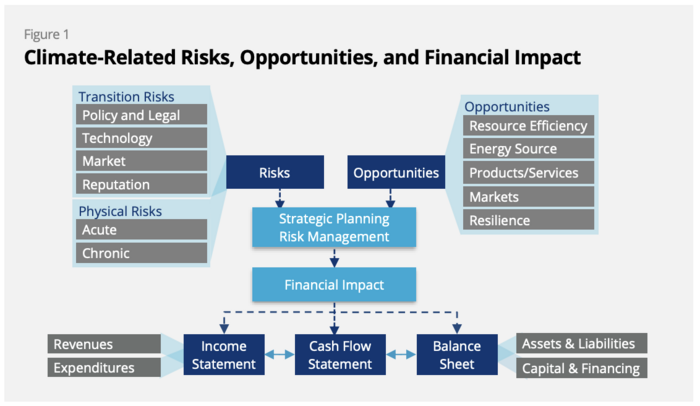
Source: Recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures
Data
References
- ↑ IPCC, 2022: Annex II: Glossary [Möller, V., R. van Diemen, J.B.R. Matthews, C. Méndez, S. Semenov, J.S. Fuglestvedt, A. Reisinger (eds.)]. In: Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [H.-O.Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke, V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA, pp. 2897–2930, doi:10.1017/9781009325844.029.
- ↑ Adger WN, Brown I, Surminski S (June 2018). "Advances in risk assessment for climate change adaptation policy". Philosophical Transactions. Series A, Mathematical, Physical, and Engineering Sciences. 376 (2121): 20180106. Bibcode:2018RSPTA.37680106A. doi:10.1098/rsta.2018.0106. PMC 5938640. PMID 29712800.
- ↑ Eckstein D, Hutfils M, Winges M (December 2018). Global Climate Risk Index 2019; Who Suffers Most From Extreme Weather Events? Weather-related Loss Events in 2017 and 1998 to 2017 (PDF) (14th ed.). Bonn: Germanwatch e.V. p. 35. ISBN 978-3-943704-70-9. Retrieved 7 December 2019.
- ↑ Ara Begum, R., R. Lempert, E. Ali, T.A. Benjaminsen, T. Bernauer, W. Cramer, X. Cui, K. Mach, G. Nagy, N.C. Stenseth, R. Sukumar, and P. Wester, 2022: Chapter 1: Point of Departure and Key Concepts. In: Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [H.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke, V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA, pp. 121–196, doi:10.1017/9781009325844.003.
- ↑ IPCC (2018). Global Warming of 1.5°C. An IPCC Special Report. Summary for Policymakers (PDF). Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. p. 5.
- ↑ Whetton P, Hennessy K, Clarke J, McInnes K, Kent D (2012-12-01). "Use of Representative Climate Futures in impact and adaptation assessment". Climatic Change. 115 (3): 433–442. Bibcode:2012ClCh..115..433W. doi:10.1007/s10584-012-0471-z. S2CID 153833090
- ↑ About — IPCC". Retrieved 2023-11-16.
- ↑ Imperial College Business School Center for Climate Finance & Investment (February 2022). “What is Climate Risk? A Field Guide for Investors, Lenders, and Regulators.” Available at: https://imperialcollegelondon.app.box.com/s/te5eahz3x47q93vufwwu3ntmf5rxecxs
- ↑ Taskforce on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (June 2017). “Recommendations of the Taskforce on Climate-related Financial Disclosures: Final Report.” Available at: https://assets.bbhub.io/company/sites/60/2021/10/FINAL-2017-TCFD-Report.pdf